Pearly penile papules (PPP) have distinguishing features that can be differentiated from other conditions that can cause penis bumps. The differentiating diagnoses include STD and non-STD related conditions that cause penis bumps.
Pearly Penile Papules Diagnosis

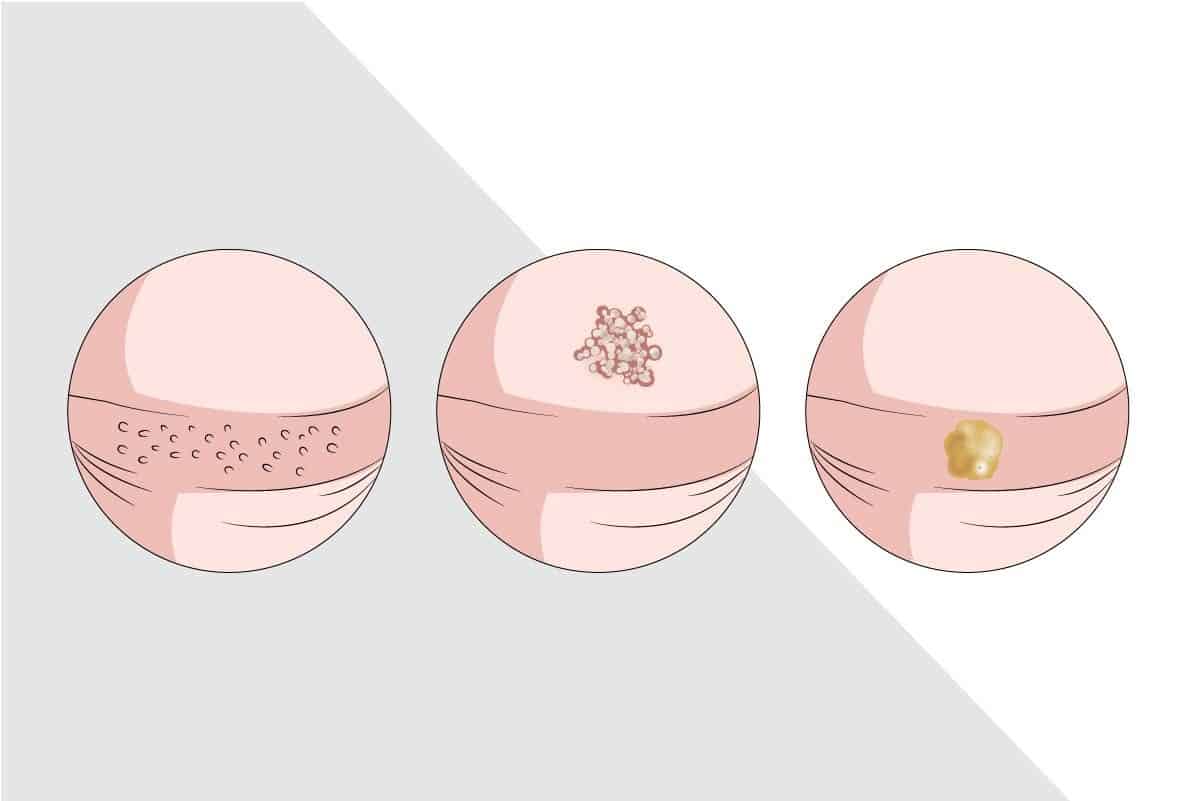
Pearly penile papules can be determined by the onset time, why they appear, the location of their appearance, what they appear as, how long they appear, and what symptoms are present. Pearly penile papules have a common distinguishing factor from other conditions of being limited to the corona and below the head of the penis on the sides of the frenulum.
- Onset Time – Pearly penile papules onset time is typically in late adolescence to early adulthood without any known or unknown exposure to viruses or bacteria.
- Why They Appear – Pearly penile papules appear because of normal anatomical variance. It is theorized the anatomical variance is from embryonic remnants.
- Location Of Appearance – Pearly penile papules normally appear in one or more rows around the corona of the glans penis, also known as the rim of the penis head, and below the head on the underside of the shaft on the sides of the frenulum. Pearly penile papules do not appear anywhere else on the body.
- What They Appear As – Pearly penile papules appear as one to four millimeter pearly, flesh-colored, or white bumps that can resemble pimples and normally in one or more rows.
- How Long They Appear – Pearly penile papules stay on the penis from the first occurrence and may have slight regression in appearance as men age.
- Symptoms – Pearly penile papules are asymptomatic.
STD Conditions
The differential diagnoses that are STDs include genital herpes and genital warts.
Genital Herpes

Photo Credit: Dermnet
- Onset Time – Genital herpes typically appears in 2 to 12 days after any known or unknown exposure to the herpes simplex virus. In some cases, genital herpes may not appear until a few weeks to years after the initial exposure.
- Why They Appear – Genital herpes appear from exposure to herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) from oral sex transmission, herpes simplex type 2 (HSV-2) from sexual intercourse, or by any skin-to-skin contact of the herpes lesions on the mouth or genitals.
- Location Of Appearance – Genital herpes can appear on the penis head, penis shaft, scrotum, thighs, rectum, anus, and buttocks in men.
- What They Appear As – Genital herpes appear as a group of fluid-filled blisters or genital ulcers.
- How Long They Appear – Genital herpes blisters typically turn to open sores that crust over and heal within 1 to 3 weeks from their first appearance or recurred appearance. Genital herpes can have a lifetime of multiple recurrences when the herpes simplex virus is not dormant.
- Symptoms – Genital herpes does not always appear as a result of having the herpes simplex virus. Genital herpes symptoms typically include itching and burning before an outbreak, headaches, aches, swollen lymph nodes, and fever. The symptoms are less noticeable in recurrent outbreaks.
Genital Warts (Condyloma Acuminatum)

Photo Credit: Dermnet
- Onset Time – External genital warts, also known as condyloma acuminatum, typically appear 1 to 3 months after any known or unknown exposure to the human papillomavirus (HPV). In some cases, it may take more than 3 months for the lesions to appear.
- Why They Appear – Genital warts appear after exposure to the human papillomavirus through oral sex, sexual intercourse, or any skin-to-skin contact with the lesions.
- Location Of Appearance – Genital warts can appear on the penis, scrotum, thigh, anus, buttocks, and groin in men.
- What They Appear As – Genital warts can appear as scattered skin-colored or darker cauliflower-like raised clusters of bumps. The bumps can also be smooth or rough and flat.
- How Long They Appear – Genital warts can go away on their own within 2 years or more because the immune system normally gets rid of the HPV infection. Sometimes treatment may be needed for warts to be removed.
- Symptoms – Genital warts do not always appear as a result of having HPV. Genital warts typically have symptoms of burning sensations and itching.
STD Or Non-STD Related Condition
The differential diagnosis that can be either an STD or non-STD condition is molluscum contagiosum.
Molluscum Contagiosum

Photo Credit: Dermnet
- Onset Time – Molluscum contagiosum lesions typically appear 2 weeks to 6 months after any known or unknown exposure to the molluscum contagiosum virus.
- Why They Appear – Molluscum contagiosum lesions appear after exposure to the molluscum contagiosum virus by using contaminated fomites (inanimate objects that can spread the virus), skin-to-skin contact of the lesions through sexual intercourse, or any other skin-to-skin contact with the lesions.
- Location Of Appearance – Molluscum contagiosum lesions can appear anywhere on the body. They appear on the genitals and/or in the genital region when they are sexually transmitted.
- What They Appear As – Molluscum contagiosum lesions can appear as 2 to 5 mm flesh-colored papules with a central depression. The papules cores may produce a cheesy material.
- How Long They Appear – Molluscum contagiosum lesions typically go away within 6 to 12 months but can take as long as 4 years.
- Symptoms – Molluscum contagiosum lesions are typically asymptomatic but can become swollen and red.
Non-STD Related Conditions
The differential diagnoses that are not STD related conditions include Fordyce spots, lichen nitidus, and sebaceous hyperplasia.
Fordyce Spots

- Onset Time – Fordyce spots on the penis typically appear in adolescence without any known or unknown exposure to viruses or bacteria.
- Why They Appear – Fordyce spots on the penis appear because of the normal anatomical variance of the sebaceous glands (glands that produce sebum normally found in hair follicles).
- Location Of Appearance – Fordyce spots typically appear on the scrotum, the penis’ underside, sides, and foreskin in men when in the genital area. They sometimes appear on the head of the penis and are not limited to the corona.
- What They Appear As – Fordyce spots appear as 1 to 5 mm visible sebaceous glands without hair follicles. Sebaceous glands with hair follicles are not considered Fordyce spots but can be located next to Fordyce spots.
- How Long They Appear – Fordyce spots may become less noticeable over time but typically stay for a lifetime unless removed.
- Symptoms – Fordyce spots are asymptomatic.
Lichen Nitidus

Photo Credit: Dermnet
- Onset Time – Lichen nitidus onset time is typically in childhood to young adulthood without any known or unknown exposure to viruses or bacteria.
- Why They Appear – Lichen nitidus underlying cause is unknown. They form on the skin because of the inflammatory response from white blood cells called T lymphocytes.
- Location Of Appearance – Lichen nitidus can appear anywhere on the body including the genital area and penis. They rarely occur on the palms of the hand and soles of the feet.
- What They Appear As – Lichen nitidus papules are skin-colored but can be lighter or darker than skin color, glistening, flat-topped, and round in appearance. They are typically pinpoint to pinhead size.
- How Long They Appear – Lichen nitidus typically goes away within a few months to a year.
- Symptoms – Lichen nitidus papules typically are asymptomatic but in some cases, the bumps may itch.
Sebaceous Hyperplasia

Photo Credit: Dermnet
- Onset Time – Sebaceous hyperplasia typically appears in adolescence without any known or unknown exposure to any virus or bacteria.
- Why They Appear – Sebaceous hyperplasia papules appear because of the normal anatomical variance of the sebaceous glands (glands that produce sebum normally found in hair follicles) becoming enlarged.
- Location Of Appearance – Sebaceous hyperplasia papules typically appear on the scrotum and the penis’ shaft in men when in the genital area.
- What They Appear As – Sebaceous hyperplasia appears as 1 to 3 mm visible enlarged sebaceous glands with or without hair follicles with a central depression.
- How Long They Appear – Sebaceous hyperplasia may become less noticeable but typically stay for a lifetime unless removed.
- Symptoms – Sebaceous hyperplasia papules are asymptomatic.
References
American Academy of Dermatology – Genital Warts
American Family Physician – Noninfectious Penile Lesions
CDC – Genital Herpes
CDC – Molluscum Contagiosum
Diagnosis and Management of Pearly Penile Papules
Fordyce Spots Masquerading as Penile Warts
Mayo Clinic – Diseases and Conditions
Papule, Pearly Penile
Penile Warts: An Update On Their Evaluation and Management
Sebaceous Hyperplasia of the Scrotum and Penile Shaft